Corrosion-Resistant Fastener Systems for Automotive & Energy Applications
Engineered fastener solutions designed to maintain structural integrity and performance in corrosive environments through strategic material selection, advanced coating systems, and rigorous validation testing.
Our comprehensive approach combines material science, surface treatment technology, and quality validation to deliver fasteners that withstand harsh environmental conditions.

What Causes Corrosion in Fasteners
Corrosion in fasteners occurs when the base metal reacts with environmental agents, leading to material degradation and loss of mechanical properties. The primary corrosion mechanisms include:
- •Electrochemical corrosion: When steel fasteners are exposed to moisture and oxygen, an electrochemical cell forms between the anode (steel) and cathode (oxygen), causing iron to oxidize and form rust.
- •Galvanic corrosion: When dissimilar metals are in contact in the presence of an electrolyte (moisture, salt), the less noble metal corrodes preferentially. For example, steel fasteners in contact with aluminum or copper.
- •Chloride-induced corrosion: Road salt, marine environments, and industrial atmospheres contain chloride ions that accelerate corrosion by breaking down protective oxide layers and promoting pitting.
- •Atmospheric corrosion: Humidity, temperature cycling, and pollutants (sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides) create corrosive conditions that degrade unprotected steel surfaces.
- •Stress corrosion cracking: The combination of tensile stress and corrosive environment can cause crack initiation and propagation, particularly in high-strength fasteners.
The rate and severity of corrosion depend on environmental factors including humidity, temperature, exposure to salt or chemicals, and the presence of crevices or contact with dissimilar materials. Understanding these mechanisms informs material and coating selection decisions. For a detailed guide on common causes of fastener corrosion and prevention strategies, see our comprehensive resource.
How Corrosion Resistance is Engineered

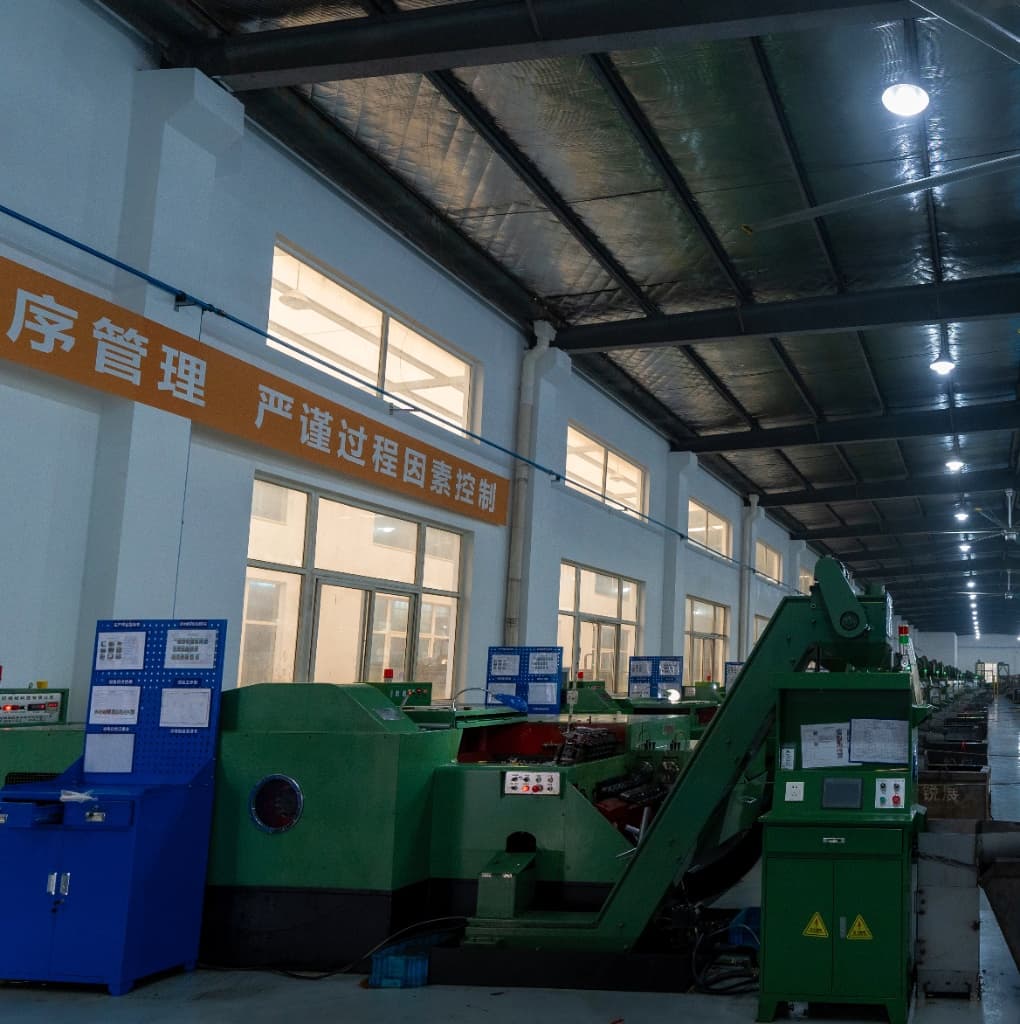
Automated Coating Process
Our automated electroplating lines ensure uniform coating thickness and consistent quality across all fastener surfaces, critical for reliable corrosion protection.
Base Material Selection
The foundation of corrosion resistance begins with appropriate base material selection. Material choice depends on mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, and cost constraints.
- •Carbon steel: Most common base material, requires protective coatings for corrosion resistance. Suitable for high-strength applications when properly coated.
- •Stainless steel: Inherent corrosion resistance through chromium oxide layer. Grades 304 and 316 offer different levels of chloride resistance. Higher cost but eliminates need for coating in many applications.
- •Alloy steel: Used for high-strength applications. Requires careful coating selection to avoid hydrogen embrittlement during plating processes.
Surface Coating Systems
Protective coatings create a barrier between the base metal and corrosive environment. Coating effectiveness depends on composition, thickness uniformity, adhesion quality, and post-treatment processes. Nickel coatings protect fasteners by forming a dense barrier layer that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the base metal. (Learn more about nickel coating corrosion protection). When selecting nickel coatings, consider the difference between electroplated and electroless nickel for optimal performance. For detailed information on nickel-plated fasteners, including performance characteristics and application guidance, see our product overview.
- •Barrier protection: Coating physically prevents contact between metal and environment. Thickness and uniformity are critical factors.
- •Sacrificial protection: Zinc-based coatings corrode preferentially to protect the underlying steel (galvanic protection).
- •Passivation: Chemical conversion layers (e.g., trivalent chromium) enhance corrosion resistance by forming stable oxide films.
- •Coating compatibility: Coating selection must consider substrate preparation, mechanical properties, and application requirements.
Process Control and Inspection
Consistent corrosion resistance requires controlled manufacturing processes and systematic quality verification at each stage of production.
- •Surface preparation: Cleaning, degreasing, and activation ensure proper coating adhesion and uniformity.
- •Process parameters: Controlled bath chemistry, temperature, current density, and immersion time ensure consistent coating properties.
- •Thickness measurement: XRF and eddy current methods verify coating thickness meets specification requirements.
- •Adhesion testing: Verification that coatings remain bonded to substrate under mechanical stress.
- •Salt spray validation: Accelerated corrosion testing confirms performance meets application requirements.
Typical Coating Options

Barrel Electroplating Process
Our barrel plating equipment ensures uniform coating coverage and optimal throughput for high-volume production, maintaining consistent quality across fastener batches.
Zinc Plating
Standard zinc electroplating provides cost-effective corrosion protection for general-purpose applications. The zinc layer acts as both a barrier and sacrificial anode, protecting the underlying steel.
- •Typical salt spray performance: 240-480 hours (Neutral Salt Spray Test)
- •Suitable for indoor applications and mild outdoor environments
- •Cost-effective solution for high-volume production
- •Available with trivalent chromium passivation (Cr3+) for enhanced performance
- •Coating thickness typically ranges from 5-15 microns depending on application
Zinc-Nickel Plating
Alloy coating containing 10-15% nickel provides superior corrosion resistance compared to pure zinc plating. The nickel content improves coating stability and reduces corrosion rate.
- •Typical salt spray performance: 720-1000+ hours (NSS)
- •Preferred for automotive, EV battery enclosures, and energy storage applications
- •Lower hydrogen embrittlement risk compared to some alternative coatings
- •Compatible with trivalent chromium passivation (Cr3+)
- •Higher cost than zinc plating but provides extended service life in harsh environments
Trivalent Chromium Passivation (Cr3+)
Both zinc and zinc-nickel plated fasteners undergo trivalent chromium passivation to enhance corrosion resistance and provide uniform surface appearance. This environmentally compliant process replaces hexavalent chromium (Cr6+) while maintaining performance standards.
- •RoHS compliant and environmentally safe alternative to hexavalent chromium
- •Forms a protective conversion layer on the coating surface
- •Improves salt spray performance by 20-30% compared to unpassivated coatings
- •Available in clear, blue, or black finish options
- •Meets automotive and industrial environmental requirements
Verification & Testing

Neutral Salt Spray Test (NSS)
The Neutral Salt Spray Test is the primary accelerated corrosion test used to evaluate fastener coating performance. Test specimens are exposed to a continuous salt fog environment (5% NaCl solution at 35°C) to simulate accelerated corrosion conditions.
Test results are reported as hours to first appearance of white rust (zinc corrosion) or red rust (base metal corrosion), depending on coating type and application requirements.
Testing Standards & Quality Control
ASTM B117
Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus. Establishes test conditions, equipment requirements, and evaluation criteria for consistent, reproducible results.
ISO 9227
Corrosion Tests in Artificial Atmospheres - Salt Spray Tests. International standard ensuring compatibility with global quality requirements and customer specifications.
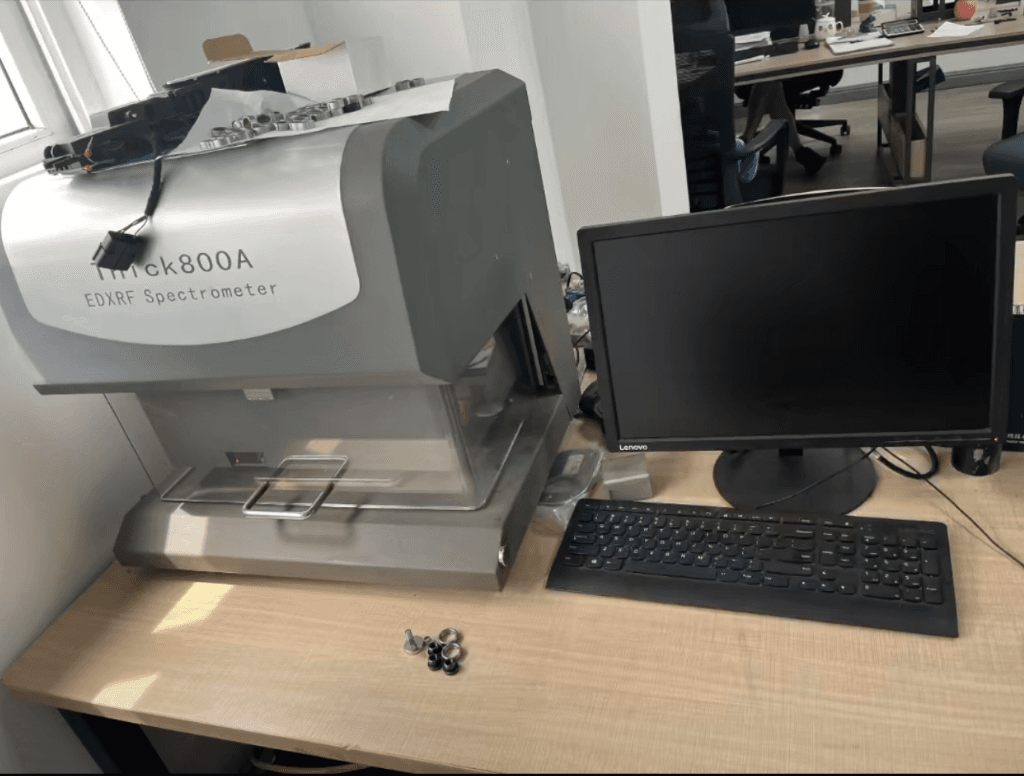

Coating Thickness Measurement
XRF and eddy current methods verify coating thickness meets specification requirements, ensuring consistent protection across all fastener surfaces.
Important: Salt spray test results are accelerated laboratory conditions and do not provide absolute guarantees of service life. Actual performance depends on environmental conditions, application factors, and maintenance practices. Test results should be used for comparative evaluation and specification compliance verification.
Typical Applications

Electric Vehicle Battery Enclosures
Rivet nuts and fasteners in battery enclosure assemblies require long-term corrosion protection due to exposure to moisture, temperature cycling, and potential electrolyte contact.

Energy Storage Systems
Outdoor battery storage containers and power systems require fasteners that maintain integrity under extended environmental exposure.

Automotive Underbody Components
Fasteners in underbody and chassis applications face road salt, moisture, and debris. Coating selection directly impacts vehicle service life and warranty requirements.

Marine & Coastal Applications
High-salt environments require maximum corrosion resistance. Zinc-nickel coatings provide superior performance compared to standard zinc plating.
Industrial Equipment
Manufacturing equipment, outdoor machinery, and industrial enclosures benefit from enhanced corrosion protection to reduce maintenance frequency.

Construction & Infrastructure
Structural fasteners in bridges, buildings, and outdoor structures require durable corrosion protection for long-term performance.
How to Specify Corrosion-Resistant Fasteners
When specifying corrosion-resistant fasteners, provide clear requirements to ensure the selected solution meets your application needs. Include the following information:
1. Environmental Conditions
- • Indoor vs. outdoor exposure
- • Presence of salt, chemicals, or moisture
- • Temperature range and cycling
- • Contact with dissimilar metals
2. Performance Requirements
- • Required salt spray hours (e.g., 720 hours NSS)
- • Expected service life
- • Mechanical property requirements (strength, torque)
- • Appearance requirements (color, finish)
3. Material & Coating Specifications
- • Base material grade (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel)
- • Coating type (zinc, zinc-nickel, etc.)
- • Coating thickness requirements
- • Passivation type (trivalent chromium Cr3+)
4. Standards & Compliance
- • Testing standards (ASTM B117, ISO 9227)
- • Environmental regulations (RoHS, REACH)
- • Industry-specific requirements (automotive, aerospace)
- • Quality certifications needed
5. Application Details
- • Fastener type and dimensions
- • Assembly method and torque requirements
- • Access for maintenance or replacement
- • Criticality of the application
Recommendation: Share technical drawings, application details, and environmental conditions with your supplier. This enables engineering teams to recommend optimal material and coating combinations, validate performance through testing, and ensure compliance with your specifications.
Related Fastener Options
Nickel-Plated Fasteners
Electroplated and electroless nickel coatings provide barrier protection with excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability. Suitable for applications requiring moderate corrosion protection combined with mechanical wear resistance.
Learn more →Zinc-Nickel Fasteners
Zinc-nickel alloy coatings (10-15% nickel) offer superior salt spray resistance through combined sacrificial and barrier protection mechanisms. Preferred for automotive, EV battery enclosures, and high-corrosion environments.
Learn more →Electroless Nickel Fasteners
Autocatalytic chemical deposition provides uniform coating thickness across complex geometries, threads, and internal features. Ideal for precision assemblies requiring consistent protection and dimensional control.
Learn more →Specify Your Corrosion-Resistant Fastener Requirements
Share your technical drawings, application details, or environmental conditions. Our engineering team will recommend optimal material and coating combinations, provide salt spray test data, and ensure your specifications are met.
Ready to Get Started?
Our engineering team is ready to help you select the right corrosion-resistant fastener solution for your application.